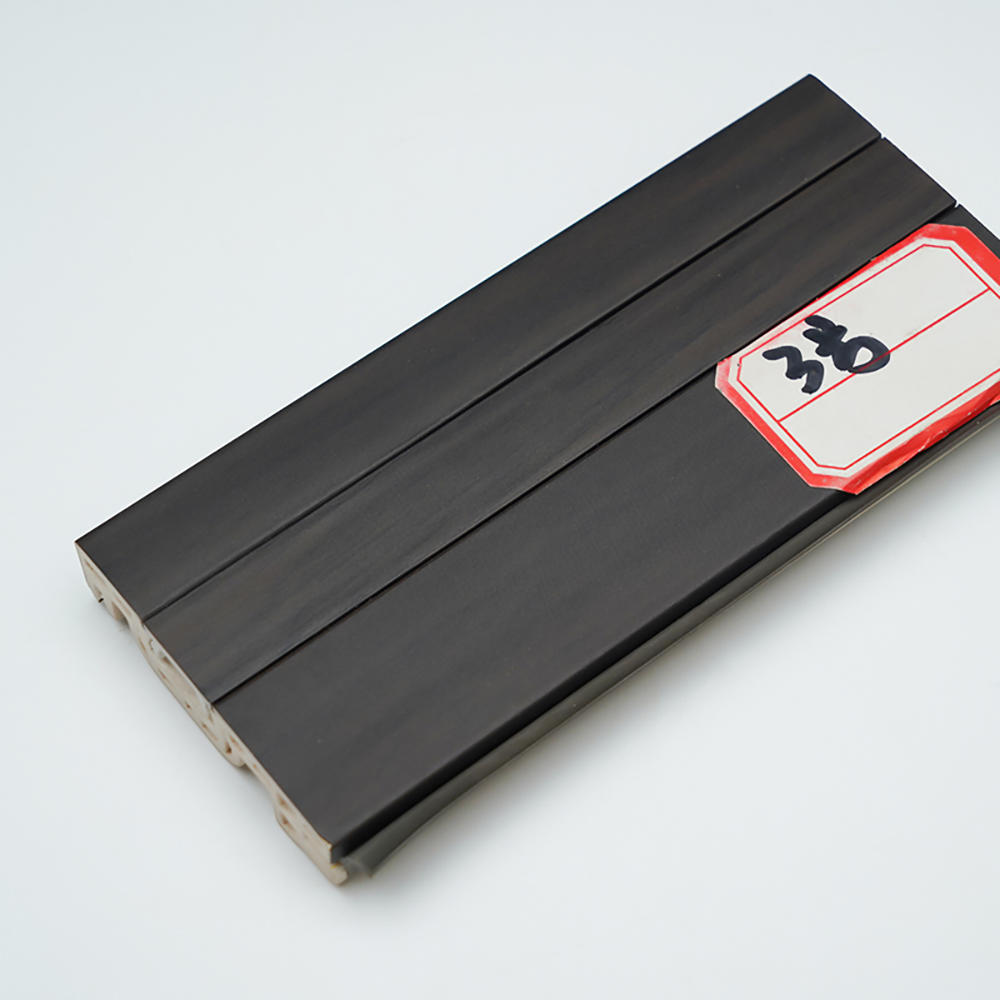
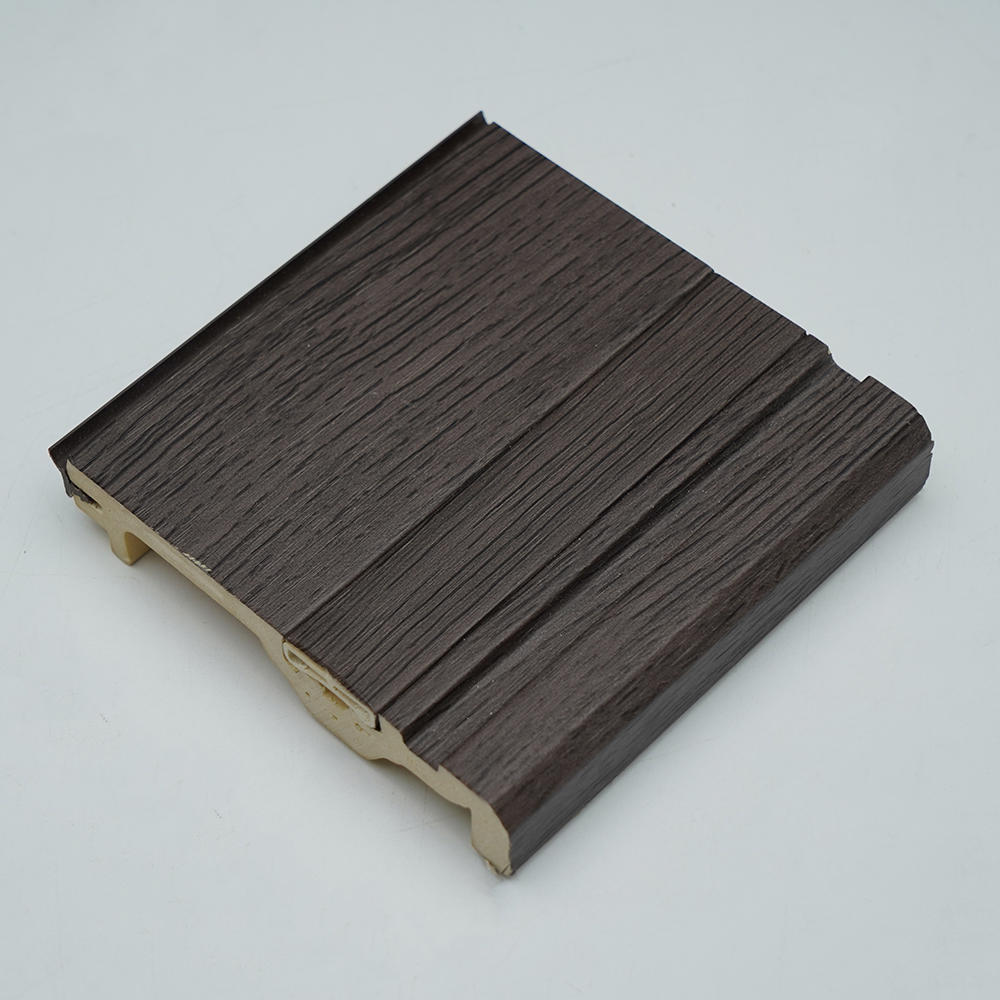
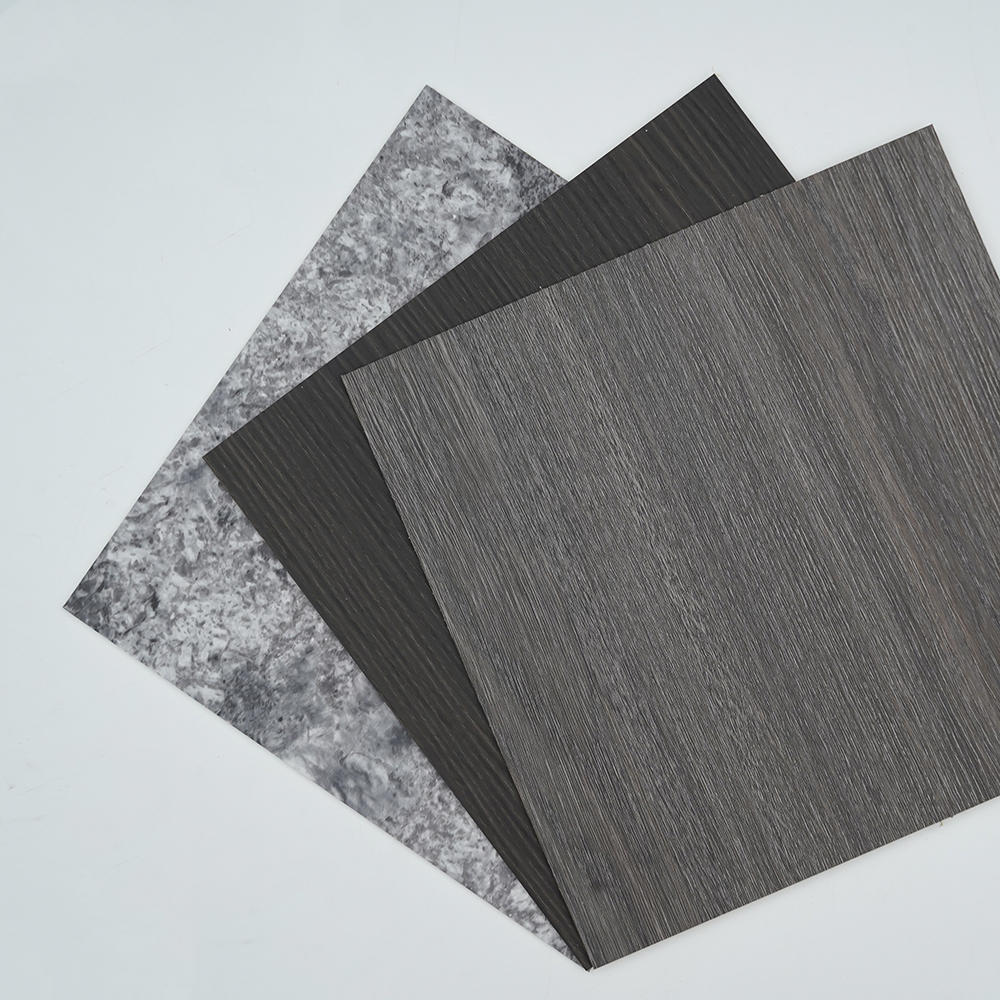
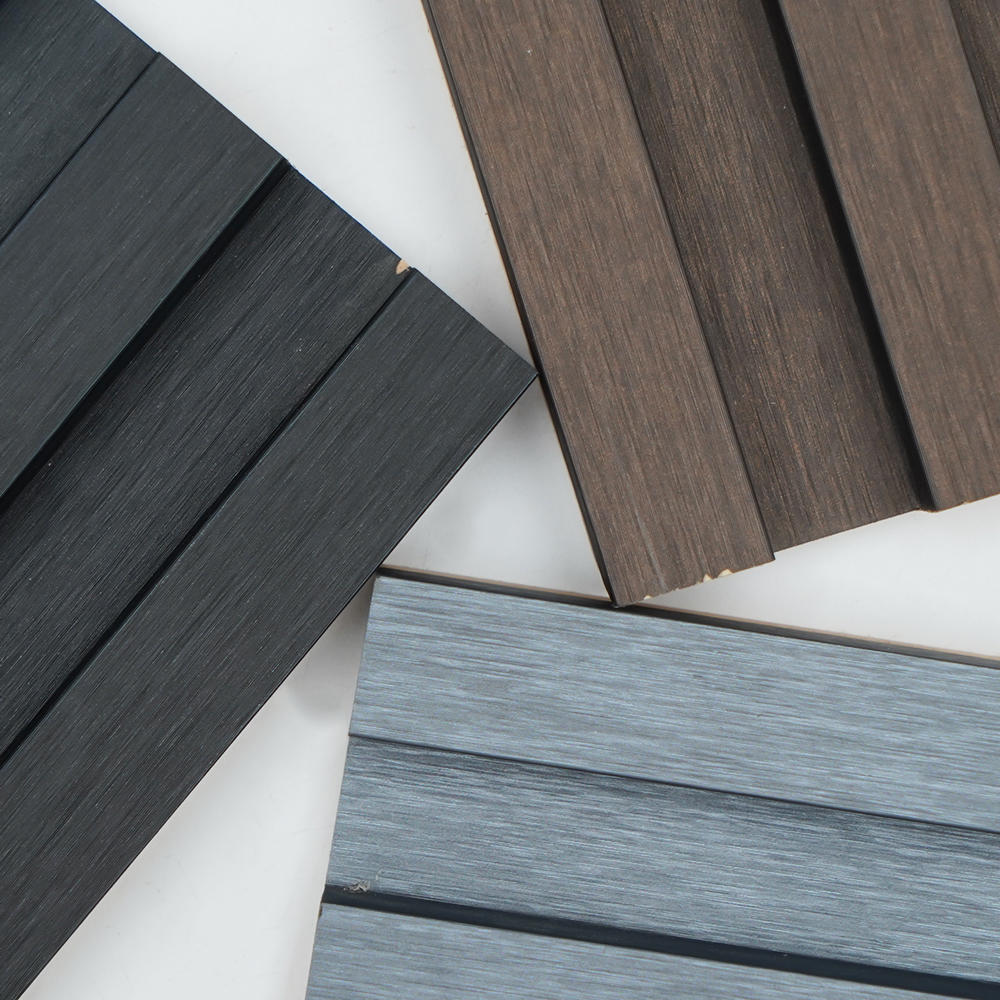
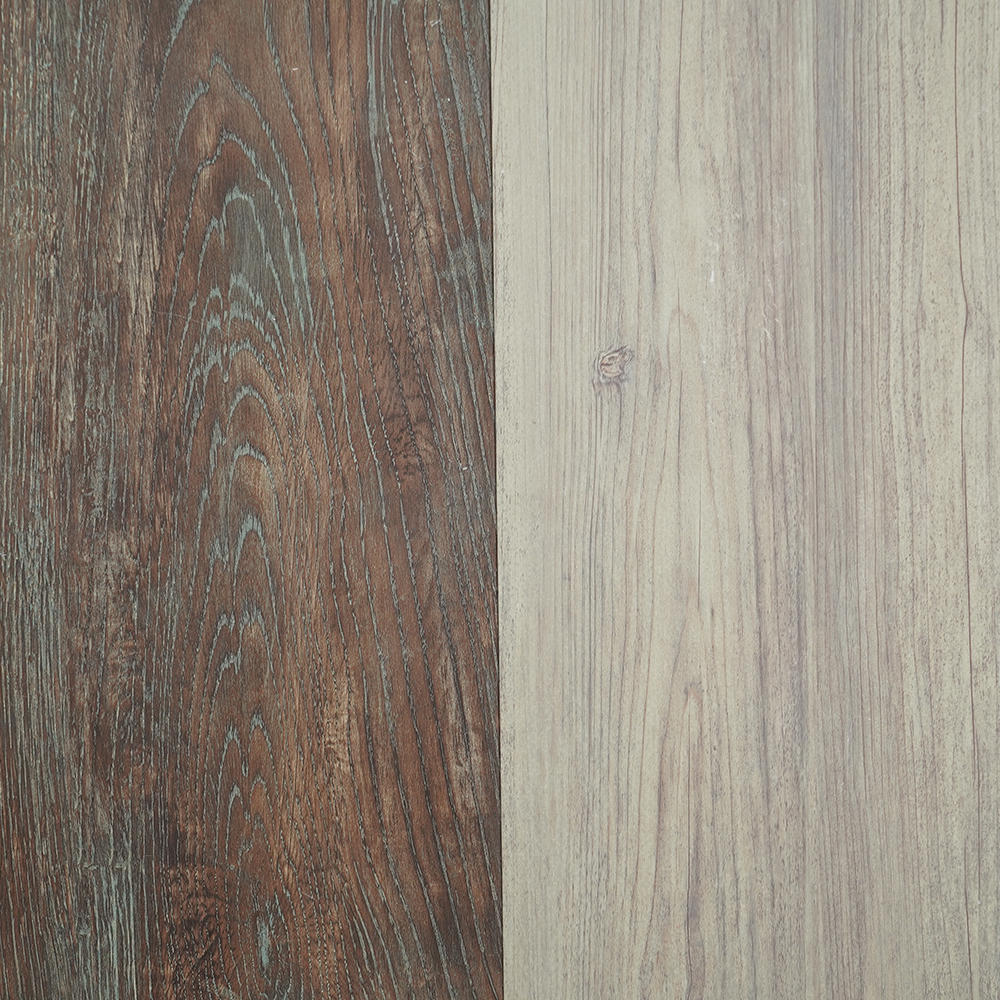
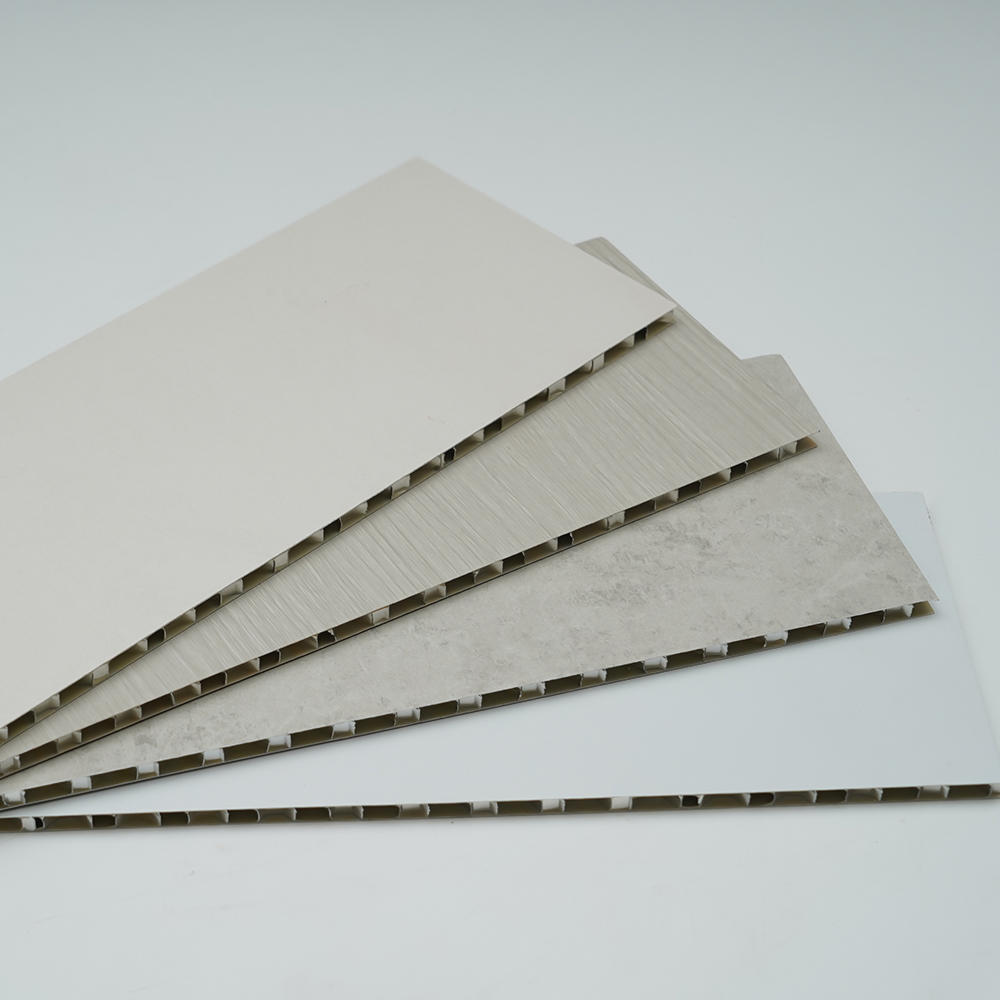
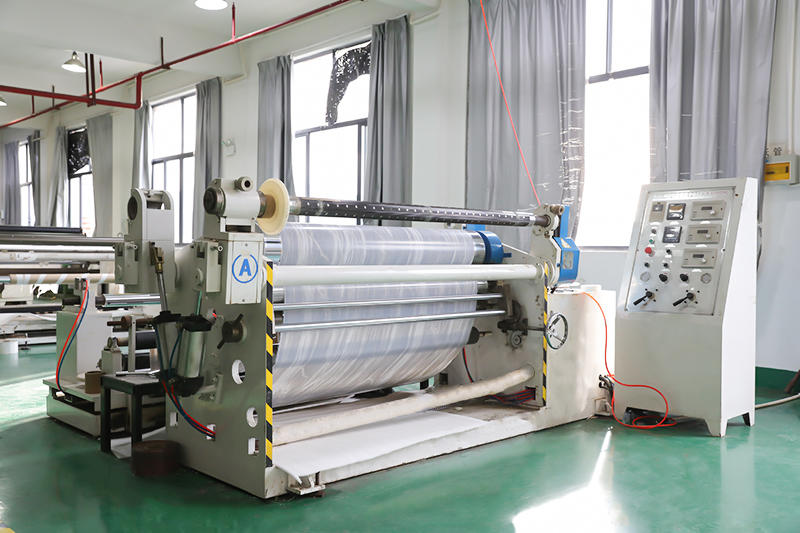
We are an industry-leading Reprocess Product factory in China. Let's make your floor look spectacular!
Showing 1-11 of 11 results
Reprocess Product Manufacturers
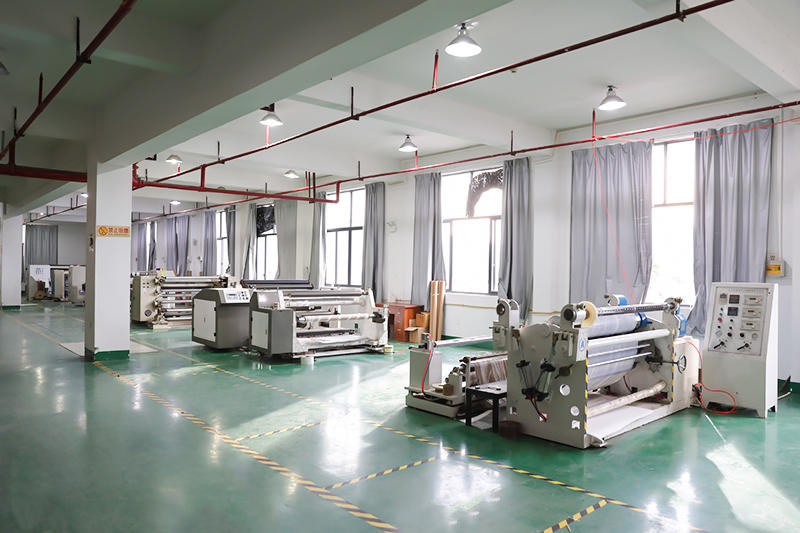
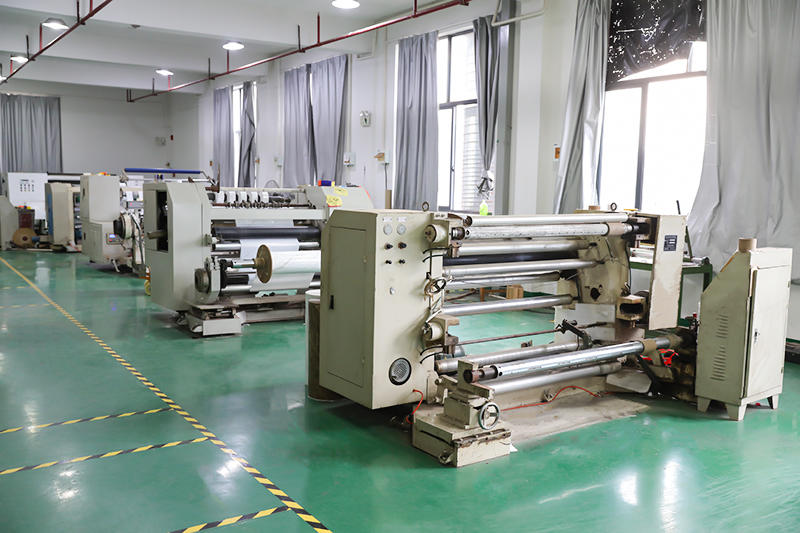
Zhejiang Zhongbang Decoration Materials Co., Ltd is China Reprocess Product Manufacturers and Reprocess Product factory, In terms of quality inspection control, we adopt the TQM model, strictly follow the AQL random inspection to ensure that each meter of the wholesale Reprocess Product meets or exceeds the industry standard and meets the needs of customers.
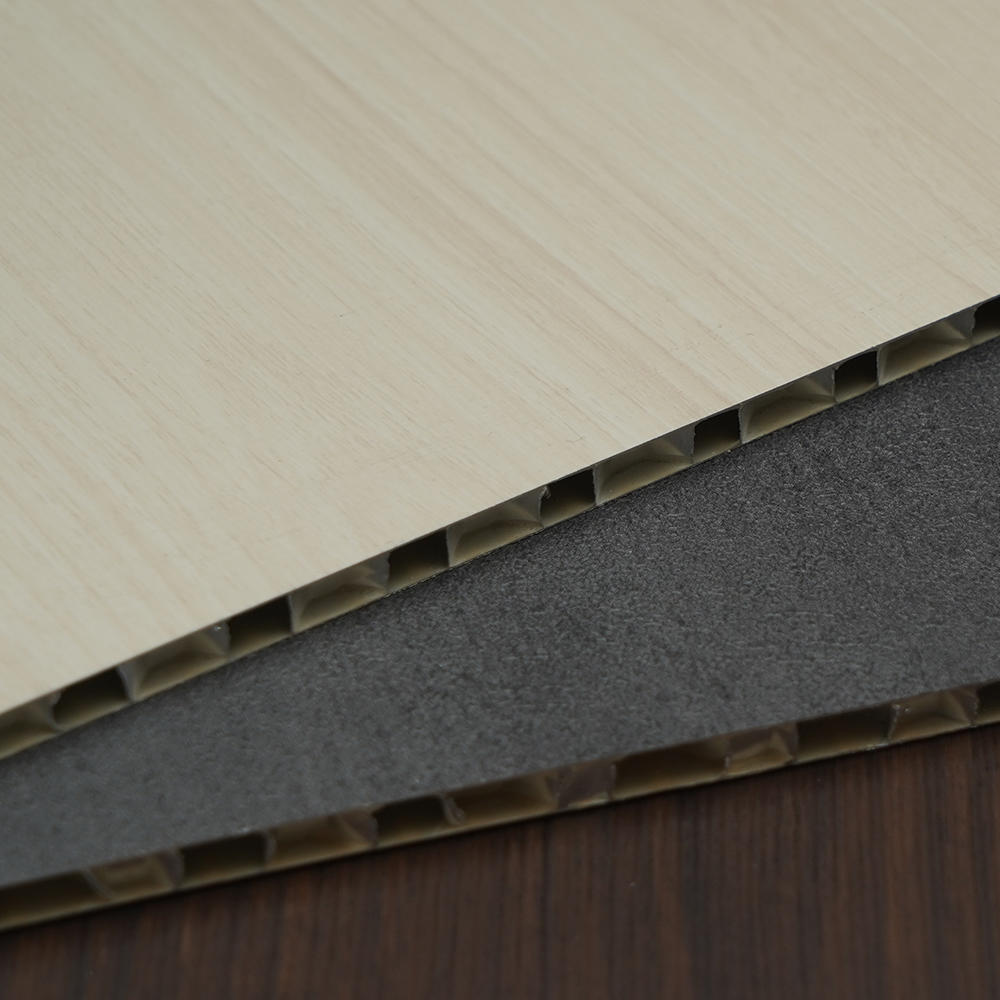
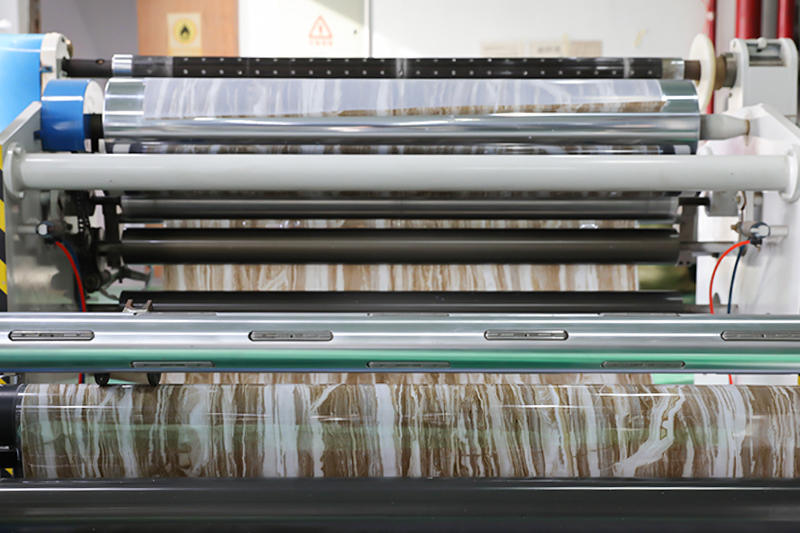
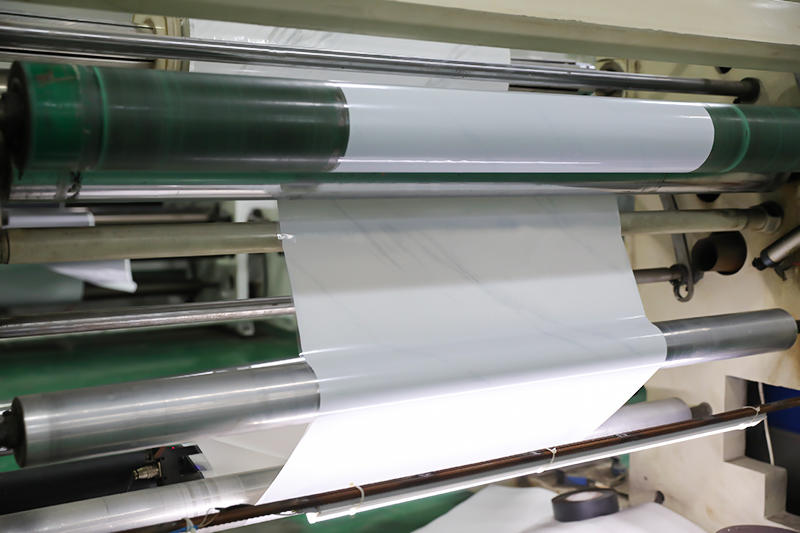
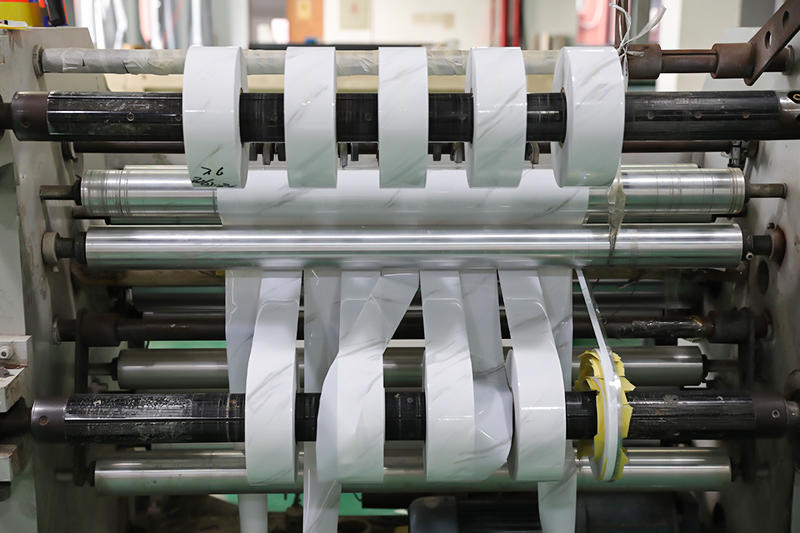
Zhongbang is mainly engaged in high-end indoor thermal transfer film , with more than 600 kinds of wood grain, marble pattern etc, which are widely used in PS, PVC stone plastic, PVC foam, metal (aluminum, steel), MDF, calcium silicate and other decorative sheets as base materials.
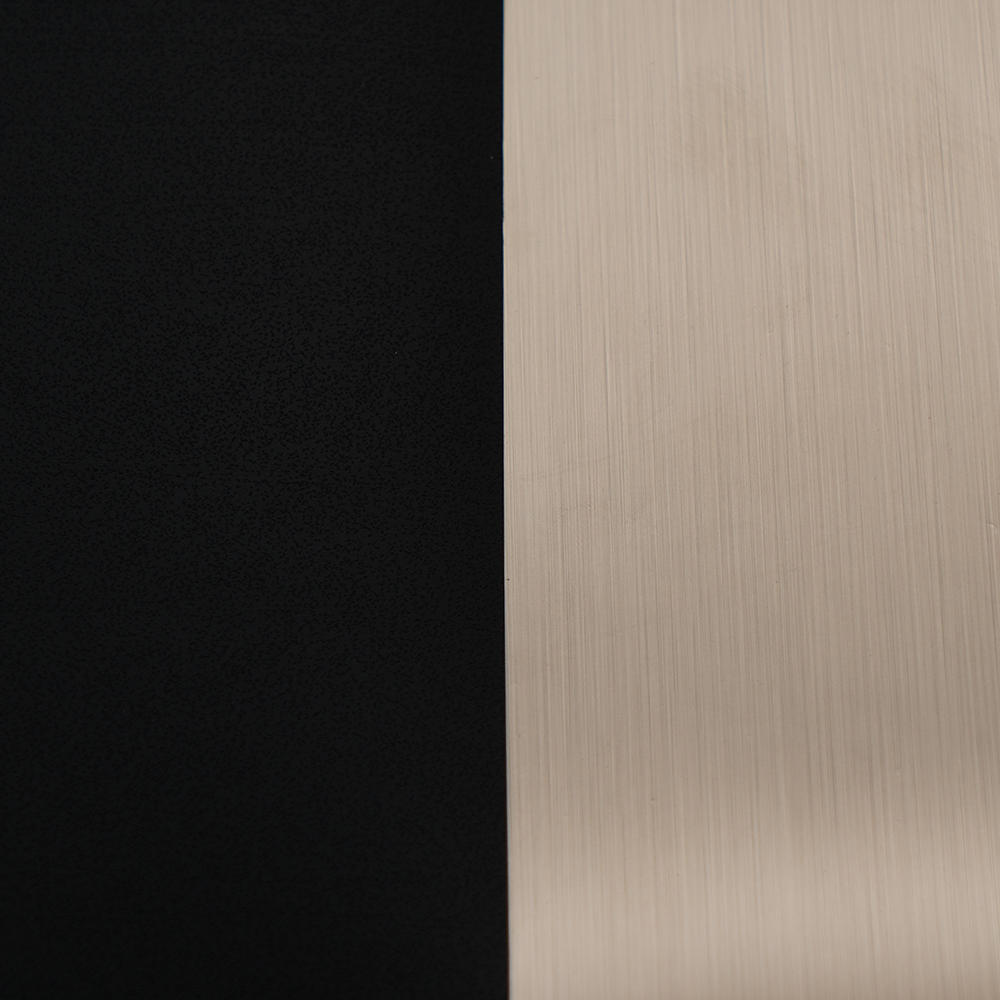
In 2017, our sub-brand "HuiChuang" was established, Huichuang is mainly engaged in high-end indoor PVC decorative film and PET decorative film, with more than 600 kinds of wood grain/marble pattern/cloth pattern/monochrome series/metal series, which are widely used in various decorative materials for wall/door/cabinet and decorative lines.
Zhongbang is mainly engaged in high-end indoor thermal transfer film , with more than 600 kinds of wood grain, marble pattern etc, which are widely used in PS, PVC stone plastic, PVC foam, metal (aluminum, steel), MDF, calcium silicate and other decorative sheets as base materials.
In 2017, our sub-brand "HuiChuang" was established, Huichuang is mainly engaged in high-end indoor PVC decorative film and PET decorative film, with more than 600 kinds of wood grain/marble pattern/cloth pattern/monochrome series/metal series, which are widely used in various decorative materials for wall/door/cabinet and decorative lines.
POPULAR CATEGORIES
Contact Info
Industry knowledge
Advantages of Reprocess Product
1. Cost savings: Reprocessing products can be more cost-effective than producing new items, as it uses existing materials and reduces waste.
2. Environmental benefits: Reprocessing helps to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, leading to more sustainable use of resources and a reduction in environmental impact.
3. Improved quality: Reprocessing can lead to improvements in product quality and performance, as manufacturers have the opportunity to identify and eliminate defects or make design improvements.
4. Increased supply: Reprocessing can help increase the supply of certain products, particularly in cases where raw materials are in short supply.
5. Consumer demand: Many consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of the products they purchase and may choose to buy reprocessed items over new ones.
Application of Reprocess Product
1. Recycling of plastics: Plastic products can be melted down and reformed into new products, reducing the demand for new plastic materials.
2. Refurbished electronics: Used electronics can be repaired and resold, reducing electronic waste and conserving resources.
3. Textile recycling: Used clothing can be recycled into new products, such as insulation or cleaning clothes.
4. Reclaimed building materials: Salvaged building materials, such as wood, brick, and metal, can be used in new construction projects, reducing the demand for new materials.
5. Agricultural waste recycling: Agricultural waste, such as crops and animal by-products, can be processed into new products, such as feed and fertilizer.
6. Automotive parts remanufacturing: Used automotive parts can be refurbished and sold as replacement parts, reducing the need for new parts and conserving resources.
How choose Reprocess Product?
1. Quality: Ensure that the reprocessed product meets the desired quality standards and specifications. This can be done by checking the manufacturer's reputation, reading product reviews, or testing the product.
2. Environmental impact: Consider the environmental impact of the reprocessing process, including the energy and resources required and any waste produced.
3. Price: Compare the price of the reprocessed product to similar new products to determine if the cost savings are significant.
4. Safety: Ensure that the reprocessed product is safe to use and meets relevant safety standards.
5. Warranty: Check the warranty offered on the reprocessed product to ensure that it is adequate.
6. Availability: Consider the availability of the reprocessed product and whether it is readily available in the desired quantity and timeframe.
7. Purpose: Consider the intended use of the reprocessed product and ensure that it meets your needs and requirements.

 英语
英语 俄语
俄语